Abstract
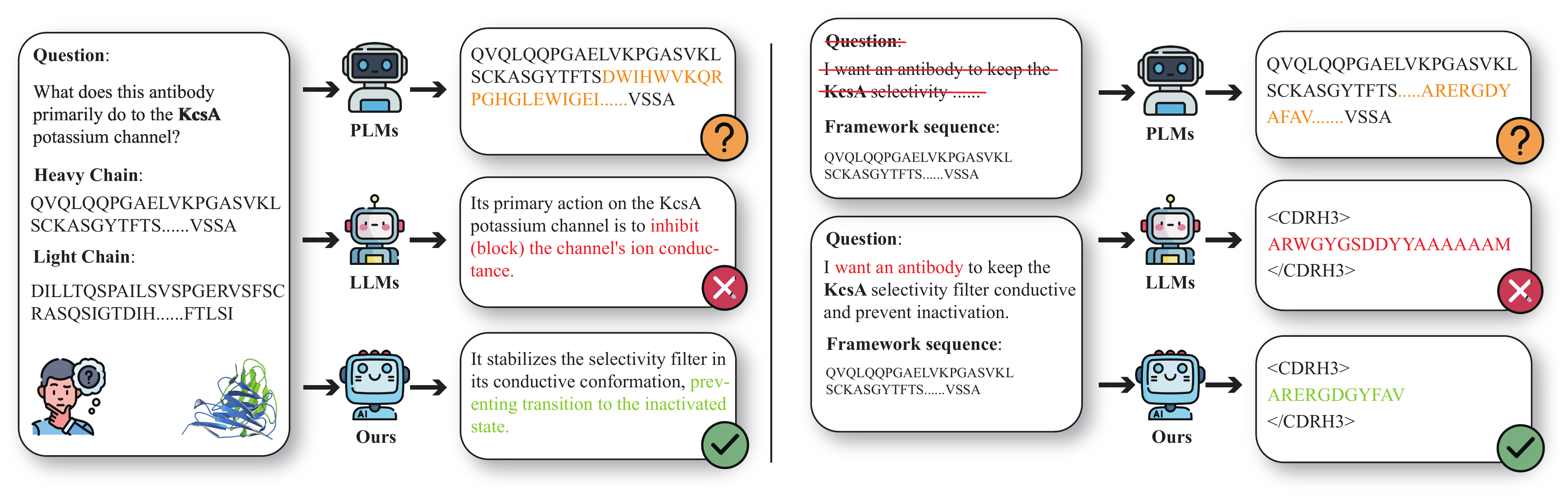
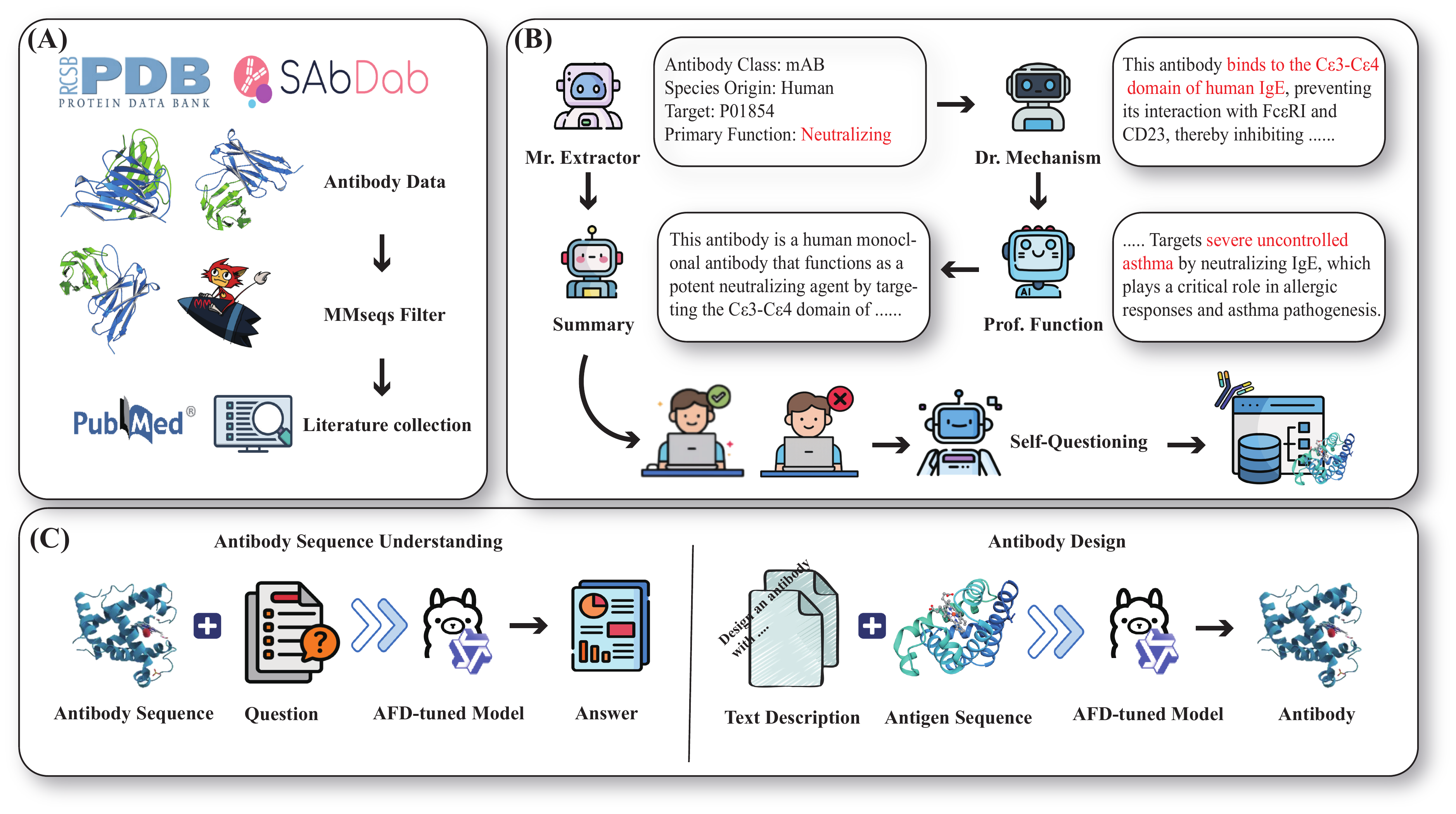
Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced protein representation learning. However, their capacity to interpret and design antibodies through natural language remains limited. To address this challenge, we present AFD-Instruction, the first large-scale instruction dataset with functional annotations tailored to antibodies. This dataset encompasses two key components: antibody understanding, which infers functional attributes directly from sequences, and antibody design, which enables de novo sequence generation under functional constraints. These components provide explicit sequence-function alignment and support antibody design guided by natural language instructions. Extensive instruction-tuning experiments on general-purpose LLMs demonstrate that AFD-Instruction consistently improves performance across diverse antibody-related tasks. By linking antibody sequences with textual descriptions of function, AFD-Instruction establishes a new foundation for advancing antibody modeling and accelerating therapeutic discovery.
Data Distribution
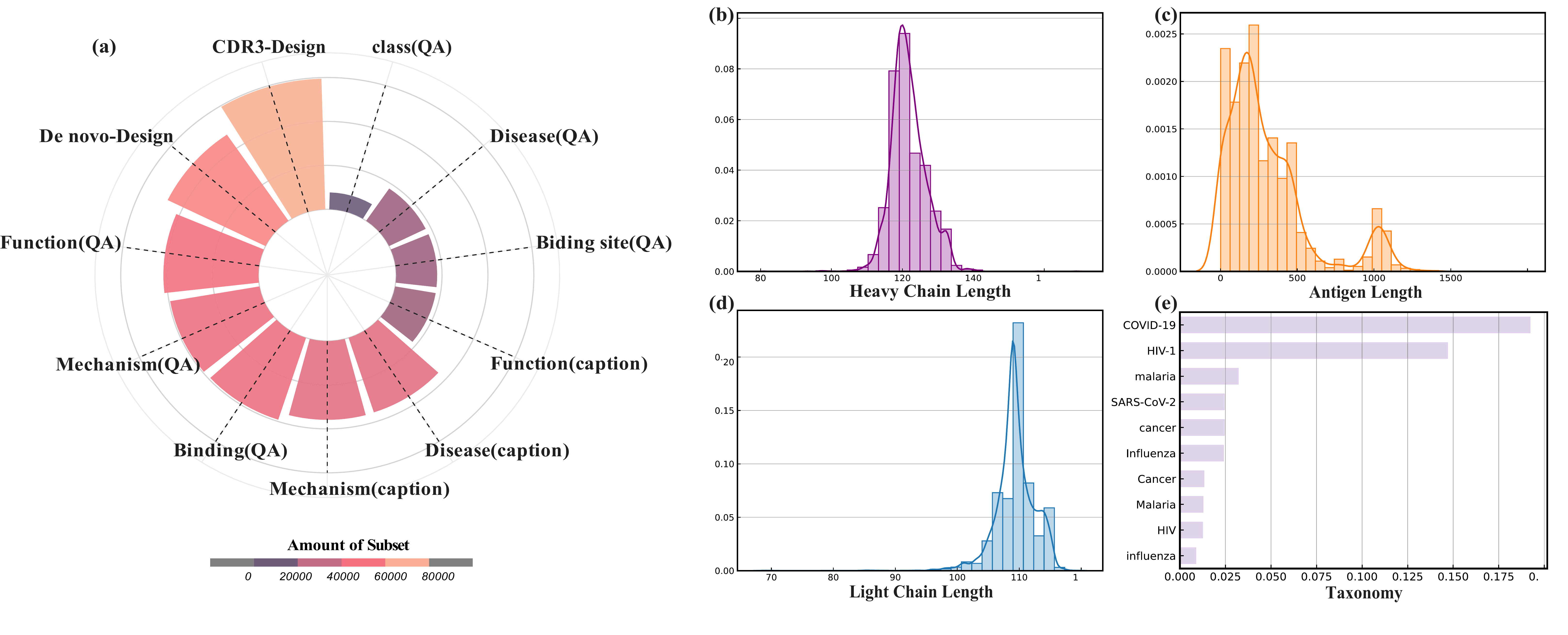
Dataset overview: (a) rose plot of instruction counts; (b) combined lengths and word analysis. The heavy-chain variable regions display a near-unimodal distribution centered around 110–125 amino acids, while light-chain variable regions are generally shorter. Antigen sequences display a broader, multimodal distribution. The corpus focuses on mechanistic/structural terms and target-focused nouns, spanning molecular to phenotypic descriptors.
Results
Antibody Sequence Understanding - Classification
Performance comparison on antibody sequence understanding tasks (classification). QwenAB and LLaMAB achieve state-of-the-art results across all subtasks including class prediction, disease association, binding prediction, mechanism inference, and functional annotation.
Antibody Sequence Understanding - Caption
Performance on caption tasks requiring free-form textual answers. AFD-Instruction-tuned models demonstrate superior performance across all evaluated metrics (BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR) compared to baseline models.
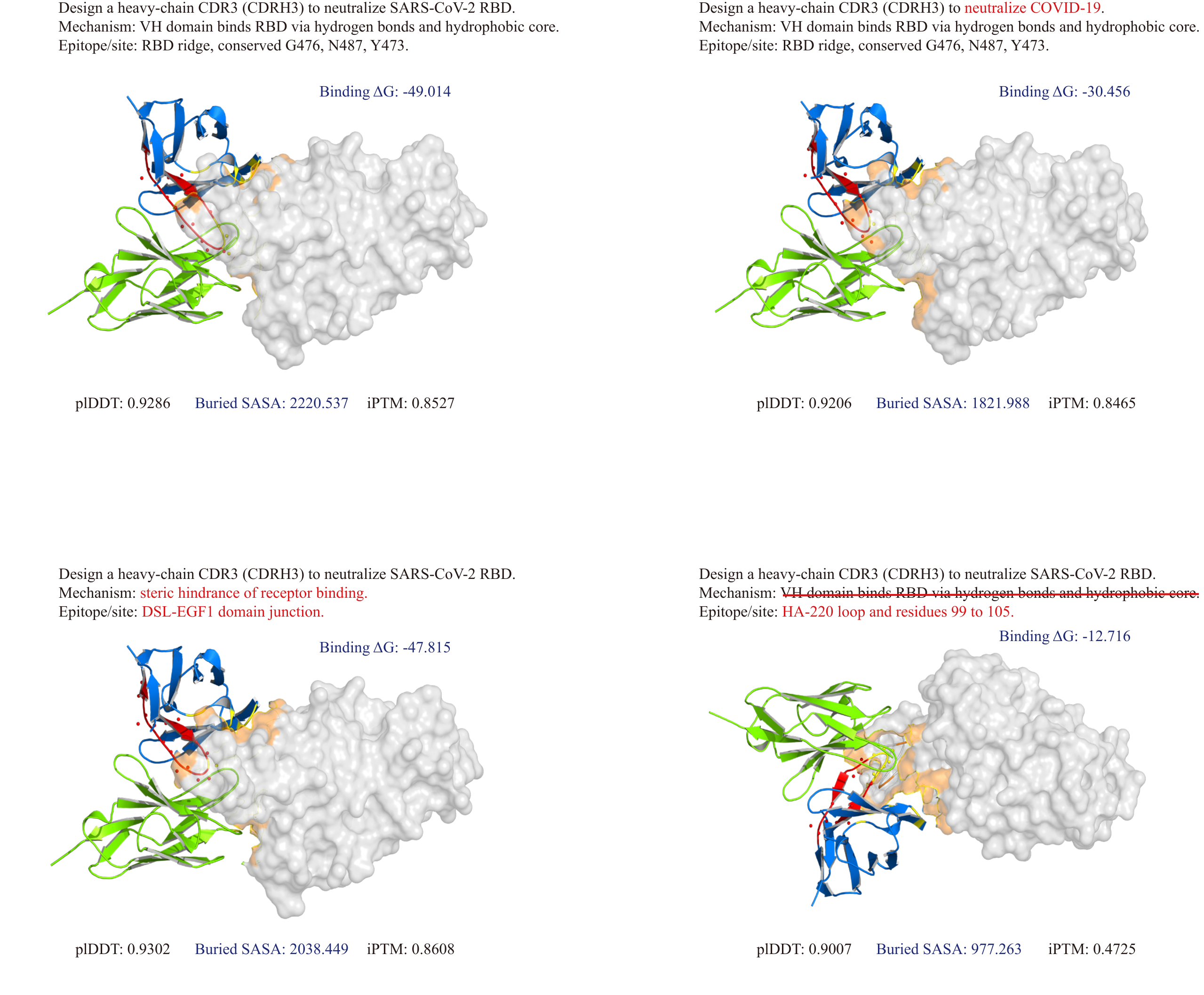
Function-Guided Antibody Design
Evaluation of antibody design quality. AFD-Instruction-tuned models achieve higher pTM, ipTM, and pLDDT scores, indicating enhanced stability, improved inter-chain packing accuracy, and increased confidence in predicted 3D conformations of designed antibody structures.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{luo2026afd,
title={AFD-INSTRUCTION: A Comprehensive Antibody Instruction Dataset with Functional Annotations for LLM-Based Understanding and Design},
author={Ling Luo and Wenbin Jiang and Hongyuan Chang and Xinkang Wang and Yueting Xiong and Mengsha Tong and Rongshan Yu},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)},
year={2026}
}